Dr S. Vangehuchten - Ear, Nose & Throat Doctor (ENT)
Medical information and surgeries
Tonsils
When do they have to be removed?
There are two reasons to have a tonsillectomy:
- The tonsils are infected,
the child is having frequent laryngitis with streptococcal infection. This is a bacterium responsible for a sore throat but also for the development of complications, such as muscular pain and arthritis, leading to acute rheumatoid arthritis, cardiac valve disease and acute nephritis. - The tonsils are too big
For this reason, they can be a hindrance for breathing and influence sleeping quality. The child is snoring, has a restless sleep or nightmares, probably starts bed-wetting again. Your child can start suffering from chronic fatigue, in many cases this may result in character changes. Swallowing becomes difficult as well. The child eats slowly and prefers eating soft food (mashed potatoes, porridge) instead of meat, for instance.
Misunderstanding
Tonsils are organs with a defensive function against infections. If we have them removed, will the child be ill more often? Do infections pass quicker to the lungs?
No.
- First of all:
If the tonsils frequently get infected with streptococci, the lymphoid tissue is destroyed to a large extend and replaced by scar tissue. The organ therefore no longer has any efficient function and, as such, has become itself a source of infection, because of which the child gets ill more often. - Secondly:
Besides the tonsils, the same lymphoid tissue is present in the whole nose and mouth area, spread underneath the mucosa. Together with the tonsils, this tissue forms the Waldeyerís tonsillar ring: a whole of lymphoid tissue against infections, of which the tonsils are just a part of. During the medical consultation, the doctor will discuss whether or not your child is due to have a tonsillectomy, based on your information, a clinical examination and sometimes also blood analysis.
Vegetations or adenoid tonsils
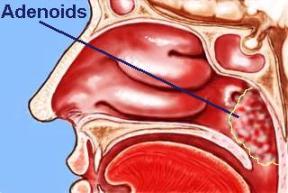
These vegetations are popularly known as polyps. In fact, a polyp is something else. When we talk about ìremoving the childís polypsî, we intend removing the adenoid tonsil. This needs to be done if the child gets a cold too often and when the adenoid tonsil has become far too big and because of this becomes a hindrance for normal breathing.
Tonsil surgeries | the practice
When a surgical operation is needed after consultation with your attending practitioner, a date is set for your hospitalization. You can partially prepare this hospitalization at home beforehand.
Preparation | Sometime before the surgical operation
In consultation with your doctor, a number of preliminary examinations have to be carried out before undergoing a surgical operation:
- Non routine: blood analysis or other extra tests.
- People more than 50 years: ECG
- People more than 60 years: blood sampling to check kidney and liver functioning, check-up on white and red blood cells and blood platelets.
Preparation | 14 days before the surgical operation
If you are taking anticoagulants (aspirin, Asaflow) or anti-inflammatory agents (Brufen, Nerofen, Apranax,...), you should stop taking these about 14 days before the surgical procedure. This medication disturbs blood-coagulation. Some of these anticoagulants have to be replaced by injections. Talk about it with your attending practitioner.
Preparation | A few days before the surgical operation
In case of diabetes, you must stop taking glucophage, metformine or metformax three days before the surgical operation. You can start taking these medicines again the day after the surgical operation.
Your hospitalization
- One day hospital stay | We are expecting you at 6:45h at the AZ Jan Portaels
- Long term hospital stay | We are expecting you at 7 oíclock at the AZ Jan Portaels.
Directives
Fasting - smoking
From midnight before your hospitalization and continuing (day of admission = day of the surgical operation) you are not allowed to eat or drink, including water or coffee. Smoking disturbs blood circulation in the operation area and hinders healing.
Medication
If youíre taking medication for your blood pressure, youíre allowed to take these with a sip of water.
No other medication should be taken if not prescribed by the doctor.
What do you need at admission
Medical info
The preoperational questionnaire. At the preliminary consultation, youíll receive this questionnaire. Please fill in all required fields and hand it over together with any other extra examination results.
Registration
- Your identity card and SIS-card.
- Your insurance documents
- Your bank card, as there is an advance to be paid.
Logistics
Nightclothes, toilet requisites, towels and washcloths and home medication.
Things you better not take with you
The AZ Jan Portaels tries its hardest to prevent theft, but the hospital remains a public place where everyone has full access. For this reason it is better not to bring valuable objects with you. If these should be really needed during your stay, you can always hand them over to be kept in a safe.
The surgical operation
Preoperational | before the surgical operation
The care team of the nursing department will prepare you for the operation checking certain parameters: blood pressure, pulse and temperature. After these standard measurements, youíll be dressed in an operation gown and should remove all make-up (including nail polish), jewels, glasses, contact lenses and dental prosthesis.
Post operational | After the surgical operation
After the surgical operation, youíll be monitored for a while in the recovery area of the operating room. When you are conscious again after the narcotics wear out, youíll be brought back to the nursing department.
On regular base, certain parameters such as blood pressure, pulse and temperature will be checked.
| It is not allowed to eat or drink immediately after the operation.
Moistening the lips is allowed. Eating and drinking are gradually introduced again during the period following the operation. Optimal pain reduction is obtained after the surgical operation. If youíre still suffering from a lot of pain, you can
request extra pain medication.
After the surgical operation
Nutrition
The day of the surgical operation
- In the evening: soft yoghurt or ice-cream.
2nd day
- Soft lukewarm food: mashed potatoes, spaghetti, pancakes, soft bread,...
- No granular food such as cornflakes, chips, gingerbread,...
- No carbonated (sparkling) drinks.
- No orange juice.
Possibility of subsequent bleeding
There is a risk of subsequent bleeding after the surgical operation. This risk is most present during the first week after the surgical operation, but it is also a possible risk during the second week. For this reason, it is recommended to stay close
to the hospital during this period.
You can possibly vomit brown, digested blood on the day of the surgical operation. This is normal and should not be a reason for concern. However, if you are vomiting fresh blood, you should immediately go to the Emergency Service of the hospital.
Pain
Pain can easily continue during the week and radiate to the ears. Paracetamol is the only analgesic that can be taken in this case.
Ear infections
Why do children have ear problems?
Otitis or effusion in the middle ear are often caused when the Eustachian tube, connecting the nose with the ear, is not yet fully developed and doesn’t allow sufficient air to pass through.
What are the symptoms and complications of otitis media?
- pain,
- fever, convulsions,
- necessity for frequent use of antibiotics that results in resistance development and other disadvantagesoodzaak tot frequent antibioticagebruik met resistentieontwikkeling en andere nadelen
- hearing loss and delayed speech development
- ruptured eardrum with possible lasting eardrum perforation
- mastoiditis or inflammation of the petrosal bone behind the ear
- meningitis
- concrescence and retraction of the eardrum, with possible forming of eardrum cysts (cholesteatoma), which can afflict hearing many years later by destroying the ossicles. Such cholesteatoma always requires a substantial operation and hearing recovery cannot be guaranteed
What are ear tubes and when do they have to be inserted?
These are small plastic tubes that are introduced in the eardrum of children under a short sedation or general anesthesia. They can be inserted on adults after consultation and under local anesthesia.
They allow air into the ear so the ear can heal. They normally remain for about two years, but early rejection is possible. You are not allowed to swim under water if you have ear tubes.
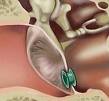
- In many cases there is a waiting period of some months in cases of hearing loss, to allow for spontaneous healing
- If the child is suffering pain or having fever too often however, the decision can be made to intervene earlier
- In case of a beginning eardrum dysgenesis, there is no waiting period
Advantages of ear tubes
Usually there are significantly less or even no cases of otitis any more.
If an otitis turns up, it is usually not causing pain, the risks are lower as the pus can flow out of the ear, and the ear can be treated with ear drops through the ear tube, this way avoiding frequently taking antibiotic syrups.
They diminish the possibility of developing a cholesteatoma in a substantial way.
Risks
In very rare cases, the eardrum tube is rejected very suddenly, leaving a hole in the eardrum. When no spontaneous healing takes place, an operation is necessary to close this hole again. This complication is rather rare and is nothing compared to the risk of a developing a cholesteatoma by not inserting ear tubes
The nose
The nose is not used exclusively for smelling, however important this nose function may be, it is an organ with a number of very important functions. The air we breathe is warmed, humidified and cleaned in the nose. More than 95% of polluting particles are filtered and eliminated in this way. This means that the nose guarantees breathing in the best possible circumstances. Besides, the nose has an important function as it determines vocal resonation and also draining of tears takes place through the nose.
Surgical operations of the nose
The most common functional surgical operations of the nose are:
Septoplasty or nose septum correction
The nose function can be influenced in many ways, for instance by a cold or due to an allergy (hypersensitivity). These dysfunctions of the nose are often worsened due to an anomalous shape of the inner nose.
septum nasaliis
The most common cause is deviation of the nasal cartilage or septum nasalis separating the two nasal cavities. This anomalous form of the nasal cartilage is very common and is often the cause of a whole series of complaints, such as a sense of nasal obstruction, difficult respiration and headaches. Straightening the nasal cartilage is a surgical operation that is very often executed. This surgical operation aims at improving the nasal functioning.
In order to stabilize the straightened nasal cartilage, nasal tampons are used, which are laterally introduced in the nose. Although this causes a stuffed up nose after the surgical operation, it usually causes little or no pain at all.
After removing the tampons, it is very important to follow up the post operational directives of the attending practitioner (no blowing, no nose picking, avoid physical efforts, no alcohol, preferably no smoking,... ) in order to avoid complications such as cartilage bleeding, infections or bad wound healing.
Sinus operations | ESS or FESS (Functional) Endoscopic Sinus Surgery | Sinuses are air-filled cavities that are drained by cilium (fine hair) in the mucosa. The air can enter the cavity through small openings, which can be stuffed as a result of mucosa swelling. In case of chronic problems, the infected mucosa will be removed by means of an endoscope and the openings of the sinus cavities will be enlarged working from inside in the nose.
The sinuses are located in the cheeks, in between the eyes and underneath the brains. Although endoscopic surgical operation on the sinuses can be considered a delicate surgical operation, there is no post operational pain in most cases. Of course it is extremely important to follow the pre and post operational directives of the attending practitioner very carefully.
Operation of the nose and sinuses | The practice
Preparations
When a surgical operation is needed after consultation with your attending practitioner, a date is fixed for your hospitalization. You can partially prepare this hospitalization at home beforehand.
Sometime before the surgical operation
In consultation with your doctor, a number of preliminary examinations have to be done before undergoing a surgical operation:
- CT-scan of the sinuses.
- Non routine: blood analysis or other extra tests.
- People more than 50 years old: ECG.
- People more than 60 years old: blood sampling to check kidney and liver functioning, check-up of the white and red blood cells and blood platelets.
14 days before the surgical operation
If you are taking anticoagulants (aspirin, Asaflow) or anti-inflammatory agents (Brufen, Nerofen, Apranax,...), you should stop taking these about 14 days before the surgical procedure. This medication disturbs blood-coagulation. Some of these anticoagulants have to be replaced by injections. Talk about it with your attending practitioner.
5 days before the surgical operation
Preoperational medication | Some patients should start with preoperational medication prescribed by the attending practitioner. This medication has to be taken until the evening before the operation, and normally has to be continued the day after the operation.
Diabetes | In case of diabetes, you must stop taking glucophage, metformine or metformax three days before the surgical operation. You can start taking these medicines again the day after the surgical operation.
Hospitalization | The operation day
- One day hospital stay | We are expecting you at 6:45h at the AZ Jan Portaels.
- Long term hospital stay | We are expecting you at 7 o’clock at the AZ Jan Portaels.
Fasting
From midnight before your hospitalization and continuing (day of admission = day of the surgical operation) you are not allowed to eat or drink, including water or coffee.
Smoking and medication.
Smoking disturbs blood circulation in the area of the operation and hinders healing. If you’re taking medication for your blood pressure, you’re allowed to take these with a sip of water. No other medication should be taken if not prescribed by the doctor.
What do you need at admission
The preoperational questionnaire. At the preliminary consultation, you’ll receive this questionnaire. Please fill in all required fields and hand it over together with any other extra examination results.
Your identity card and SIS-card, your insurance documents, your bank card (as there is an advance to be paid).
Nightclothes, toilet requisites, towels, washcloths and home medication.
Things you better not bring with you
The AZ Jan Portaels tries its hardest to prevent theft, but the hospital remains a public place where everyone has full access. For this reason it is better not to take valuable objects with you. If these should be really needed during your stay, you can always hand them over to be kept in a safe.
After the surgical operation
Nasal tampons may have been laterally inserted during surgery. If this is the case, you will also have nasal packing, where some nasal mucus is penetrating. This packing is to be replaced on regular base.
Nasal surgery with tampons
Nasal tampons should always remain three nights in the nose to give sufficient support to the nasal cartilage in order to have it stabilized. The tampons also serve to stop bleeding. As long as there are tampons in the nose, some blood can drip from the nostrils or into the throat. Sometimes there is even some blood coming through the lachrymal canal into the eyes. This is nothing serious. Operations on the nose and sinuses are not very painful for the most part. In case of severe pain, eyelid swelling or impression of visual disturbance, you need to inform your attending practitioner.
If tampons have been used, you are usually not allowed to go home until the day after the surgical operation. Home medication is started again the day after the surgical operation. Healing can be more or less quick, but you should take into account that there are about three post operational check-ups at the attending practitioner’s. You have an appointment with the attending practitioner the third day after the surgical operation for removing the nasal tampons.
Activities
You are not allowed to do any physical efforts or blow your nose for the ten days beginning from the day of the surgical operation. These can both cause internal hematoma in the nasal cartilage, and this would make a new operation necessary.
You can start working again 14 days after the surgical operation. As for swimming, it is better to wait even a bit longer
Extra advice
It is possible that you have more tears in your eyes. There is also a chance for more sneezing fits. Be careful! Always sneeze with your mouth open, so to restrict the pressure in the nose and to avoid the tampons to be blown out.
Nasal surgery without tampons
When no nose tampons have been used for the operation, you’ll have a nasal wash immediately after the operation, as soon as you are well awake for the first time in the recovery room and you can blow your nose. You should continue doing this in your own patient room every hour. If you did not wake up too late after the anesthesia, in certain cases you may even go home the same day.
At home
Starting the day after the surgical operation up to the day of the check-up appointment at the attending practitioner’s, you should practice nose rinsing every 3-4 hours. In case of home medicines, you should continue taking these.
Check-up appointments and activities
The number of check-up appointments, return to work or starting sports and swimming should be discussed with the attending doctor as these depend on the extend of the surgical operation.
Tympanoplasty
Tympanoplasty or surgical reconstruction of the eardrum (tympanic membrane).
A subcutaneous graft is taken under complete anesthesia and used to repair the perforation of the tympanic membrane. A bandage is applied and should not be removed for 1 week, washing your hair or doing sports is not allowed for 2 weeks, and you cannot go swimming or take a plane for 2 months.
Surgical operations for snoring
Snoring is a complex problem. It is caused by obstruction of the respiratory tract due to a stuffed up nose, a uvula that is too long or swollen tonsils, by being overweight, etc.
Snoring is not only a noise problem for the partner; it can also cause poor sleep quality, fatigue and even high blood pressure.
An operation is not a solution for everyone who snores. A thorough clinical examination, and if needed also a sleeping test, will point out whether or not you can be helped through a surgical operation.
Other
It goes without saying that only the most common surgical interventions are illustrated, meaning this list is not exhaustive. You can apply for diagnosis and start a cure for all complaints related to ear, nose, throat, neck and balance problems. Many problems can be solved using appropriate medicines, which reduces the need for a surgical intervention.